Landslides mudflows creeps and slumps are examples of mass movement. A place where a river ends.
Continental Drift And Plate Tectonics Let S Talk Science
Distance and direction of an objects change in position.
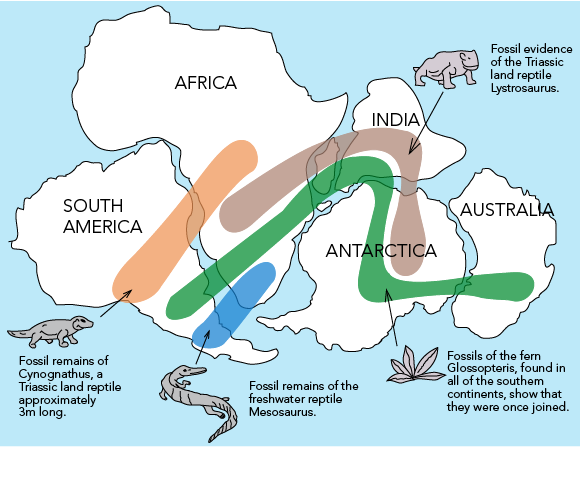
. Continent - one of the large landmasses of the earth. Septic leaks can trigger slides and excessive logging can promote mass movements. The theory of continental drift is most associated with the scientist Alfred Wegener.
Mass Movement is the downhill movement of cliff material under the influence of gravity. Plate tectonics from the Late Latin. Photograph from Pictoral Press.
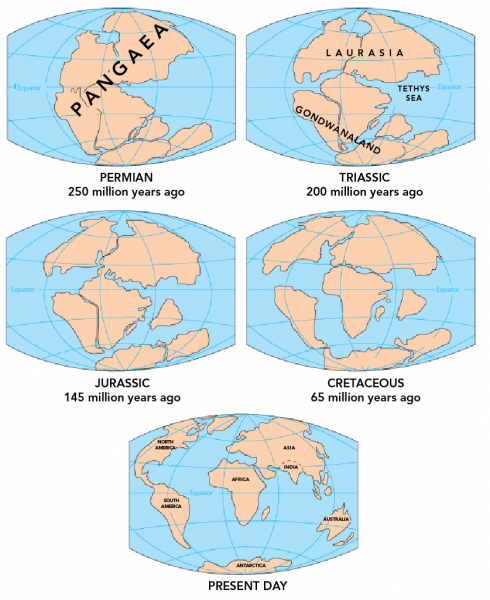
Continental Drift Theory aka tectonic theory Explains how forces in the planet create land forms made by Alfred. Separation occurs along discontinuities such as fractures joints and bedding planes and movement occurs by free-fall bouncing and rolling. Theory of Plate Tectonics.
Explain the term gradient. Evidence for competing theories continues to change the ways we understand our prehistoric roots. There is a range of different types of mass movement.
The Land Bridge Theory. The realization that Earths land masses move was first proposed by Alfred Wegener which he called continental drift. The confirmation of a strait between Asia and North America fueled an interest in the possibility of a wide plain that might have connected the two continents.
The theory of island biogeography states that the number of species found on a particular undisturbed island is determined solely by the number of species immigrating to the island and by extinction rates. Scraping action of particles suspended in wind. Caused by plate movement and measured on the Richter scale.
These are explored below. Rocks shaped by wind-blown sediment. Distance divided by time.
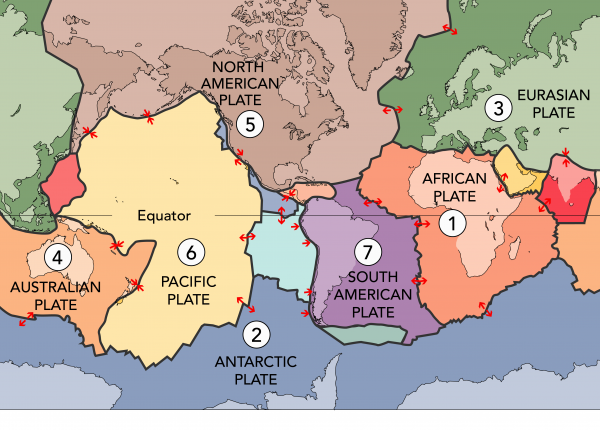
Pertaining to building is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earths lithosphere to comprise a number of large tectonic plates which have been slowly moving since about 34 billion years ago. The theory also states that isolated species may follow evolutionary routes that are different than species on land masses that are not isolated. He is shown here at the base camp for Johan Kochs 1912-1913 Greenland expedition.
Explain the term human activity. In todays world the peopling of the Americas is a hotly debated topic. Falls are abrupt movements of masses of geologic materials such as rocks and boulders that become detached from steep slopes or cliffs.
Result of competition between uplift and erosion. Construction can make a slope unstable. Examples of Divergent Boundary.
Like the scientists before us we will now merge the ideas of continental drift and seafloor spreading into the theory of plate tectonics. While evidence of animal migration is more solidified the human story may be more complicated. -mass movement is faster when the slope is steep.
The lowering of the land surface caused by the. The model builds on the concept of continental drift an idea developed. For the purposes of this theory an island is defined as more than just a piece of.
When the earths surface is pulled apart which creates parallel faultsWhile the plates spread apart the block between the separated faults drops down into the asthenosphereThe block creates a centra valley called the rift. Movement of a stationary object. They occur when rock and soil slide down a steep slope.
Total distance traveled divided by total time of travel. Human activities can contribute to factors that cause mass movement. Theory of Island Biogeography.
Mass movement also called Mass Wasting bulk movements of soil and rock debris down slopes in response to the pull of gravity or the rapid or gradual sinking of the Earths ground surface in a predominantly vertical direction. Explain the term water content. The term describes an ecosystem that is isolated by being surrounded by different ecosystems.
Land mass - a large continuous extent of land. A narrow piece of land connected to two larger land masses. Formerly the term mass wasting referred to a variety of processes by which large masses of crustal materials are moved by gravity from one place to.
-Adding or subtracting elevation. In the early 20th century Wegener published a paper explaining his theory that the continental landmasses were drifting across the Earth sometimes plowing through oceans and into each other. --Driven by surface processes.
Fall of rocks at high elevations in steep road cuts or on shores. He called this movement continental drift. Name for the slant of a line on a graph.
When the concept of seafloor spreading came along scientists recognized that it was the mechanism to explain how continents could move around Earths surface. Tectonicus from the Ancient Greek. Water stored behind a dam.
Land surface lowers due to removal of material. To make new space for buildingsroads etcsometimespeople cut into the sides of hillsthis makes a steep slope and may cause the. ---Erosion- surface lowering by mass removal.
As of 2008 genetic findings suggest that a single population of modern humans migrated from. Magma goes upward to fill in the cracks of the blockA new crust is formed by this boundary. Briefly describe what falls are.
Mudflows them are rapid downhill movements caused by a mixture of soil rock and water. Landslides are the most destructive form of mass movement. Beginning in the early 1800s American scientists and naturalists started investigating archeological sites on the east coast of the United States slowly working.
Theory that describes movement of land masses. There are seven continents. It also may generate a tsunami.
Island biogeography also called insular biogeography provides some of the best evidence in support of natural selection and the theory of evolution. Water makes the regolith heaviercausing it to move quickly down a slope. The most basic reason is the angle of repose or slope of the.
Plate tectonics is the theory that Earths land masses are in constant motion. ---Subsidence- vertical motion downwards. ---Uplift- vertical surface motion upwards.
Landslides may occur in highway cuts through hills or mountains. Terms in this set Shaping the Earth Surface. Mass movement often called mass wasting is the downslope movement of a mass of surface materials such as soil rock or mud.

Plate Tectonic Theory Tectonic Plates Map Movement Boundaries Cea
0 Comments